![]()
One of the most important materials for today’s design and building process, sold under marketing terms for clarity, strength, and durability is glass. Not all glass is the same: tougher, tempered, laminated glass all have characteristic-ones relevant to its applications, such as safety, thermal resistance, or structural integrity. Becoming acquainted with each of these forms of glass will provide a good starting point for making an effective selection when trying to pick among architectural and design selections.
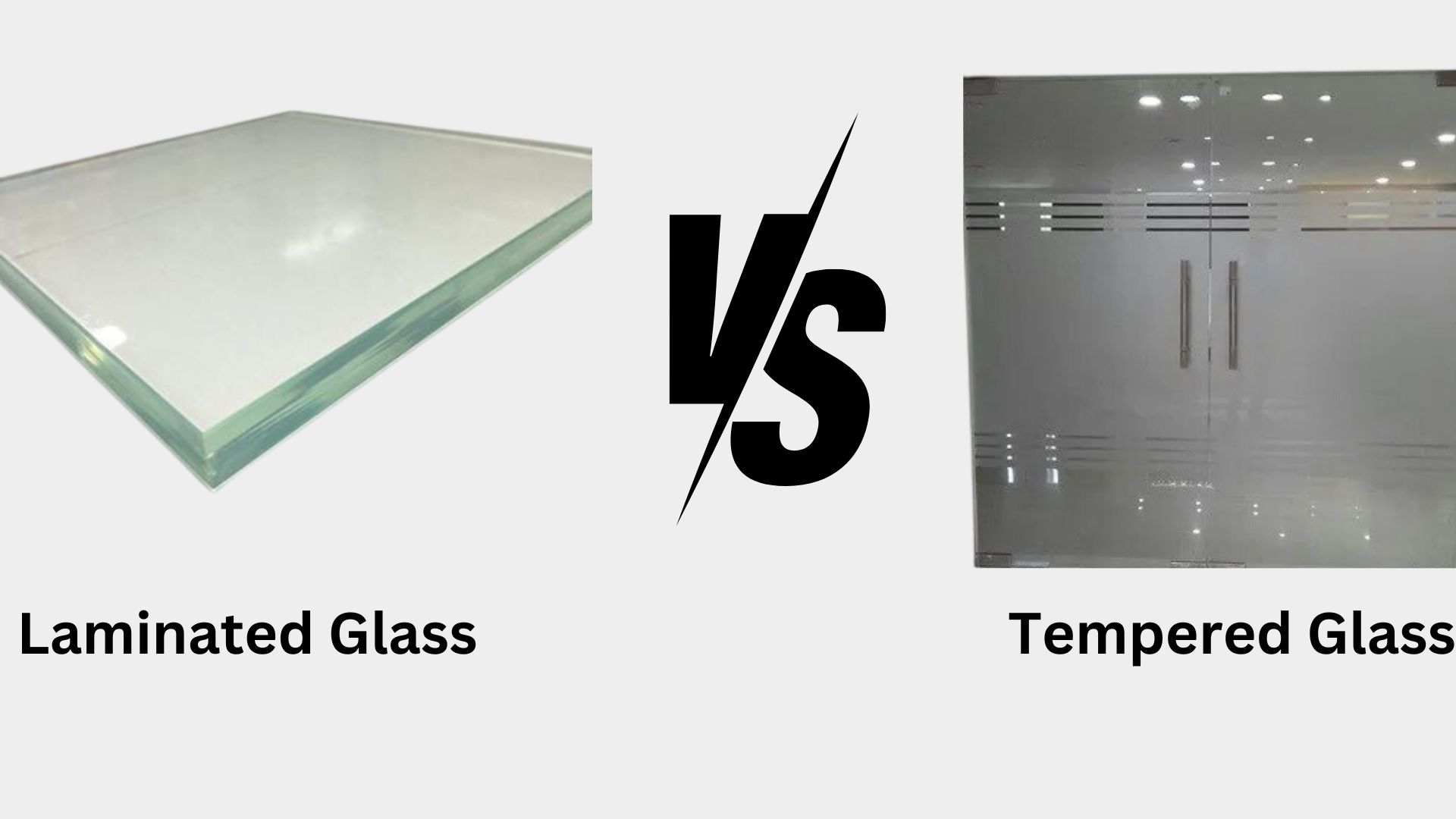
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass, also known by other names such as safety glass, is one of the safest glasses and undergoes controlled thermal and chemical treatment. It is much more potent compared to annealed glass.
How Does Toughened Glass Work?
- Heating and Cooling: Glass is heated to nearly 700 degrees and then quenched.
- Compression Layers: Exertion causes compression on the surface with strain inside.
- Safe Breaking: Fragments of laminated glass break into blunt small pieces instead of razor-sharp shards; therefore, it is less likely to harm people.
Applications of Toughened Glass
- Building Construction: Glass windows and doors, railings
- Structural: Glass sidewalks, glass flooring, canopies
- Thermal Applications: Insulated doors of the oven, industrial machinery
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is made of two or more layers of glass bonded or stuck together with an interlayer, most commonly produced using PVB (Polyvinyl Butyral) or EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate).
Properties of Laminated Glass
- Safety: Glass sticks to the interlayer and so never loses its shape, even when it breaks.
- UV Protection: Filters up to 99% of damaging UV rays, protecting the interior.
- Noise Reduction: Reduces noise, making it ideal for use in urban areas.
Uses of Laminated Glass
- Automobile: In windscreens to retain structural functionality during impact
- Architectural: Skylights, balconies, and stairwells
- Safety Use: Bank counters, jewelry cases, and bulletproof glass
What is Heat-Strengthened Glass?
Heat-strengthened glass is almost manufactured like toughened glass, except it cools a little more slowly. It possesses about double the strength compared to annealed glass, yet it is not as strong as toughened glass.
Comparison with Toughened Glass
- Strength: It is not as strong as toughened glass but may be suited for applications where rigidity must accompany flexibility.
- Breaking: Breaks into relatively larger fragments compared to the cubed-like fragments of toughened glass.
Applications of Heat-Strengthened Glass
- Insulating Glazing Units: For laminated safety glasses
- Thermal Glass Applications: Less likely to suffer from thermal shock compared to annealed glasses.
Differences Between Laminated, Toughened Glass
| Characteristic | Toughened Glass | Laminated Glass | Heat Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 4-5 times stiffer than annealed glass | Same strength as base glass but stronger and less prone to breakage | 2-3 times more resistant than annealed glass |
| Breaking Behavior | Shatters into safe little chunks | Shatters into larger, more hazardous pieces | Breaks into relatively larger fragments |
| Use For | Balconies, floors, areas with annealing | Skylights, safety screens, windscreens | Laminated glass sheets, areas prone to thermal shock |
| Cost | Mid-range cost | Higher due to the interlayer | Lower cost compared to toughened glass |
Laminated Glass Advantages
Characteristics of Laminated Glass
- UV Protection: Filters harmful UV rays, protecting interiors.
- Noise Barriers: Effective in noisy urban environments.
- Thermal Shock Resistance: Ideal for areas with extreme temperature changes.
Uses of Heat-Strengthened Glass
- Versatility: Offers a balance between strength and flexibility for specialty applications.
- Economic Safety Product: It is relatively cheaper than laminated glass.
Future of Strengthened Glass Technologies
- Chemical Strengthening: Involves replacing smaller ions with larger ions to allow compression without the need for heat.
- Self-Healing Glass: Coated with a layer that automatically heals scratches.
- Smart Glass Technology: Provides dynamic transparency, making it ideal for modern architectural designs.
Case Studies
Laminated Glass Skylight
- Specifications:
- Type of Glass: Double-layered laminated with PVB interlayer
- Cost: ₹3,000 per square foot
Glass Bridge Design
- Specifications:
- Type of Glass: Triple-layered laminated with toughened glass inclusion
- Safety Factor: PVB interlayers ensure no breakage or shattering
- Thermal Resistance: Heat-strengthened panels for resistance against thermal shocks
- Rough Estimate:
- Glass Material: ₹12,000 per sq. meter
- Installation and Labor: ₹2,500 per sq. meter
- Total Area: 300 sq. meters
- Total Cost: ₹43,50,000
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Energy Efficiency
- Aerogel-Infused Glass: Maximizes thermal and noise insulation, leading to high energy efficiency.
- Recyclability: A majority of different kinds of glass can be recycled, reducing landfill waste.
UV Protection and Noise Reduction
- Low-E Coatings: Fillings contain inelastic gases, offering both thermal insulation and transparent views.
- Anti-Reflective Coatings: Minimize glare and improve views in glare-intensive locations.
Toughened Glass in Thermal Shock Resistance
Modern glass technology has advanced to incorporate dynamic properties. Glass can now adapt to environmental changes with aerogel-infused panels, providing exceptional insulation.
Applications of Aerogel-Infused Glass
- Energy-Efficient Buildings: Used for acoustic purposes and extreme weather conditions.
Latest FAQs: Future of Glass Strengthening
What is Self-Cleaning Glass?
Self-cleaning glass has a hydrophobic layer that breaks down dirt and organic materials, reducing maintenance efforts.
How Does Aerogel-Infused Glass Work?
Aerogel-infused glass is used in energy-efficient buildings and walls to offer superior insulation properties.
How Do Dynamic Glass Windows Work?
Dynamic windows use electrochromic technology to adjust glass transparency, offering increased comfort and energy efficiency.
Leave a Reply